NEW CLIENT DISCOUNT
SAVE
$149
Monsieur Gazon, since 1985, the expert for lawn care in Quebec

4.5/5
with 1250+ reviews

4.5/5
with 1250+ reviews

Satisfaction guaranteed
Satisfaction guaranteed Satisfaction guaranteed Satisfaction guaranteed Satisfaction guaranteed
Really recommended, very good and great results in just 1 year!
Jessica.H
Saint-Jean-sur-Richelieu


Our lawn has never looked so good since we started doing business with M.Gazon!
Karine D.
Repentigny


I appreciate their service during the summer, because everything is included so that our lawn is very beautiful.
Vanessa C.
Blainville


Finally a service that works after trying several companies
Véronique L.
Bromont


After 2 treatments (over 2 years), we no longer have crabgrass!
Jacinthe T.
Montréal


The results are beyond our expectations after only one season.
Isabelle B.
Pierrefonds-Roxboro


Thanks to Monsieur Gazon, we have a magnificent lawn.
Michel G.
Longueuil


Since we have been doing business with Mr. Gazon, all the neighbors have asked us for their name.
Normand C.
Saint-Lazare


Really recommended, very good and great results in just 1 year!
Jessica.H
Saint-Jean-sur-Richelieu


Our lawn has never looked so good since we started doing business with M.Gazon!
Karine D.
Repentigny


Satisfaction guaranteed Satisfaction guaranteed Satisfaction guaranteed Satisfaction guaranteed
TERRA PROGRAMTM
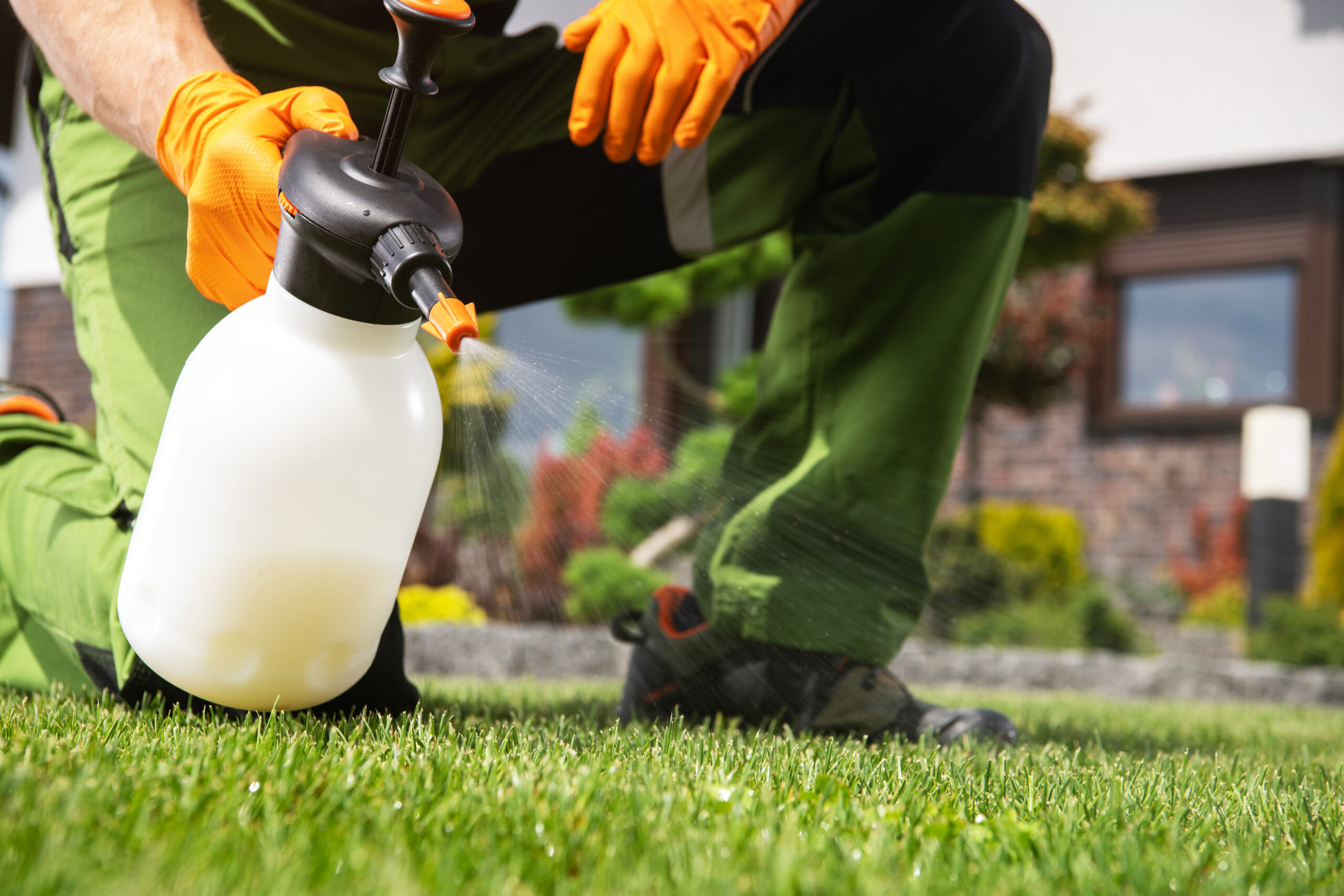
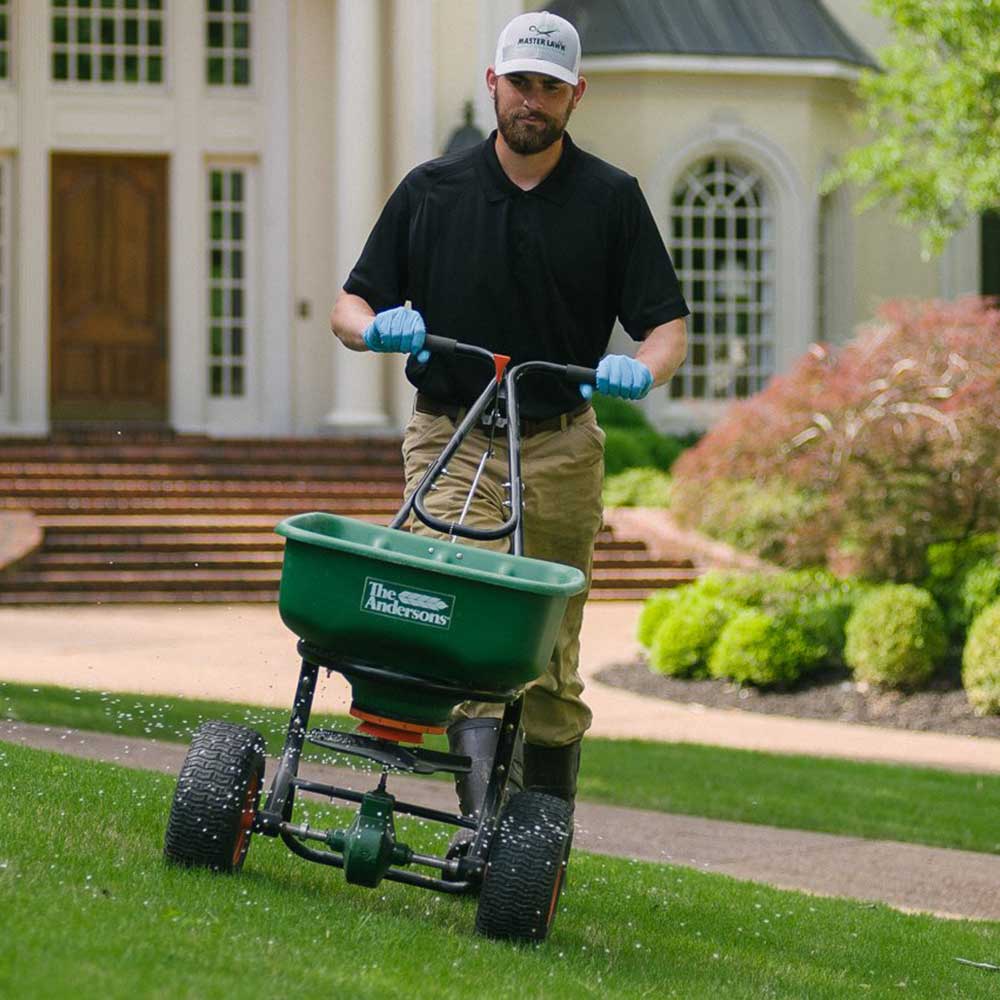
Arrosage Monsieur gazon offers you the Terra program; the highest performing professional lawn treatment in the industry. Designed by agronomists, the lawn treatment provides essential, assimilable nutrients at the right time to make your lawn green and healthy in addition to controlling weeds.
Thus, our TERRA program provides four (4) applications of slow-release fertilizer, two (2) applications of weed control, regular lawn monitoring, and an end-of-season soil NutriBoost treatment.
 Free service calls!
Free service calls!
Unlimited service calls! 1-888-348-9332